Excel to Python — Pandas Commands
Excel is one of the most popular and widely-used data tools; anyone working on computer at one time or other have come across and worked on excel sheet.
If you are looking to automate stuff in excel file using the world of Python, scripting and do automated analysis then you might have come across an incredibly popular data management library “Pandas” in python.
Pandas is built on the Numpy package and its key data structure is called the DataFrame. DataFrames allow you to store and manipulate tabular data in rows and columns.
Pandas has excellent methods for reading all kinds of data from Excel files and is better at automating data processing tasks than Excel.

In this article we will see how to use Pandas to work with Excel spreadsheets. We will cover following topics here.
- installing the necessary libraries
- reading data from excel file into pandas using python
- data exploration using pandas
- visualizing data in pandas using the visualization library “matplotlib”
- using functions to manipulate and reshape the data.
- finally, moving data back to excel.
Installation
We will use Python 3 and Jupyter Notebook to demonstrate the code in this tutorial.
If you have anaconda package manager then you can use conda install<module> command to install the required modules. For example to install pandas you will execute conda install pandas.
If you have regular non-anaconda Python installed on your machine then you can use pip install <module> command. For example, to install pandas, you would execute command pip install pandas.
The Data Set
We will use the movies data set that is available on the internet. You can download the sheet dataset from here.

This excel has 3 tabs: 1900s, 2000s, 2010s.
We will use this data set to visualize the movies with highest ratings, rating distribution, net earnings and also calculate the statistical information about the movies.
We will be analyzing and exploring this dataset using pandas library.
Reading Data from the excel
First step will be to import the pandas library.
import pandas as pdWe will use pandas read_excel method to read data from excel sheet into pandas DataFrame variable named movies.
file_path = 'https://github.com/ravijagtap/datascience/blob/main/datasets/movies.xls?raw=true'movies = pd.read_excel(file_path)
we can get the glimpse of the data using movies.head()which returns the first 5 rows from the dataset.
movies.head()
read_excel method has the ability to read the specific spreadsheets from the excel. For this read_excel takes the argument as sheetname, which enables pandas to load only the specific sheet. Alternatively if we can also load the specific sheet by sheet index and the sheet index starts from 0. If no argument is specified then by default read_excel takes index as 0.
Pandas assigns a numeric index by default for each row starting with 0. Many cases we can leave this as it is but in case if we need to have our custom index then it can be done by setting property index_col.
In below code snippet we will set the column ‘Title’ as the index column.
movies1900s = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name=0, index_col=0)
movies1900s.head()
Lets read the other 2 sheets from the excel
movies2000s = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name=1, index_col=0)
movies2000s.head()
movies2010s = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name=2, index_col=0)
movies2010s.head()
Lets combine these 3 data set into a single dataframe as they have same structure. We cam use concat method for this as below and check the number of rows using shape method on the combined dataset
movies = pd.concat([movies1900s, movies2000s, movies2010s])
movies.shape
ExcelFile class
We can also make use of ExcelFile class to work with multiple sheets in an excel spreadsheet.
xlsx_file = pd.ExcelFile(file_path)
sheets = []
for sheet in xlsx_file.sheet_names:
sheets.append(xlsx_file.parse(sheet))
movies = pd.concat(sheets)
movies.shape
Data exploration using pandas
Now that we have our moviesdataset we can explore the data using pandas library.
In excel we can do lots of function mainly like
- sorting on a column
- filtering based on some condition
- plotting graphs
- apply statistical formulas, etc.
We will do similar operations on our moviesdataset.
Sorting
Lets check the top 10 movies with highest IMDB ratings, for this sort the dataset by on column IMDB Score using sort_valuesfunction.
sort_by_rating = movies.sort_values(['IMDB Score'], ascending=False)
sort_by_rating['IMDB Score'].head(10)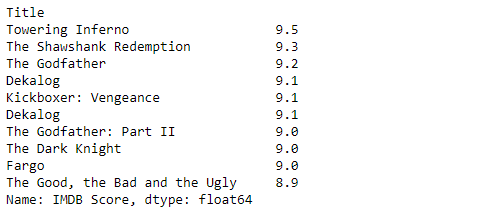
We can also visualize our data for which Pandas provides a visualization library called matplotlib. First import the library
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltWe will draw a bar chart to show the top 10 movies with their IMDB ratings as IMDB ratings is a numerical variable.
sort_by_rating['IMDB Score'].head(10).plot(title="Movies with Top 10 IMDB ratings", kind='bar', figsize=(10,7))
Filtering
Using pandas we can do filtering by applying conditions on column of a DataFrame. The result will be a Series which can be converted to DataFrame.
For example, filter all the movies with IMDB Rating ≥ 9 in USA.
usa=movies[(movies['Country']=='USA') & (movies['IMDB Score']>=9)]
Statistical Information
Statistical information of the dataset can be viewed usingdescribemethod.
movies.describe()
This method displays below statistical information for numerical columns in the dataset.
- total count of record for each column
- mean
- standard deviation
- min and max value
- the first (25%), second (50%) and third (75%) quartile
We can also check the same of individual column as well, example
movies['Gross Earnings'].mean()
Other statistical information can also be calculated and stored as new column in the dataset.
For example we can calculate the net earnings of each movie by substracting Budget from Gross Revenue and storing it in new column Net Revenue
movies["Net Earnings"] = movies["Gross Earnings"] - movies["Budget"]sort_by_net_revenue = movies.sort_values(['Net Earnings'], ascending=False)sort_by_net_revenue["Net Earnings"].head(10).plot(title="Top 10 movies by Net Revenue", kind='bar', figsize=(10,7))

Pivot Table
Lets say we have to identify the Gross Earnings per year. This can be achieved in excel using pivot table where row will be year and Gross Earnings will be summed. Same can be achieved using pandas as well.
First we need to select the set of columns that will be part of the pivot table. This is similar to selecting a Table/Range of data on which Pivot needs to be generated.
movies_subset = movies[['Year', 'Gross Earnings']] Once the columns are selected we can use the pivot_tablemethod to aggregate Gross Earnings per Year, by providing Year column as the index column.
earnings_by_year = movies_subset.pivot_table(index=['Year'])earnings_by_year.head()

We can visualize this on a line chart as below
earnings_by_year.plot(title="", kind='line', figsize=(12,7))
Similarly, we can show Gross Earnings by country and language as below
movies_subset = movies[['Country', 'Language', 'Gross Earnings']]
earnings_by_country_and_language = movies_subset.pivot_table(index=['Country', 'Language'])
earnings_by_country_and_language.head(20).plot(kind='bar', figsize=(12,7))
Exporting the result to Excel
We can export Pandas dataframe to excel using to_excelmethod.
movies.to_excel('movies_output.xlsx', index=False)we can also use ExcelWriterclass to output DataFrames to excel with most advance control.
excel_writer = pd.ExcelWriter('movies_output.xlsx', engine='xlsxwriter')movies.to_excel(excel_writer, index=False, sheet_name='Consolidated')workbook = excel_writer.bookworksheet = excel_writer.sheets['Consolidated']excel_writer.save()

Conclusion
As a data scientist you will find Pandas as handy tool for exploring, cleaning, transforming, and visualization of data in Python.
Some useful resources for learning Pandas.
